What Should You Know About Meltblown Nonwoven Fabric?
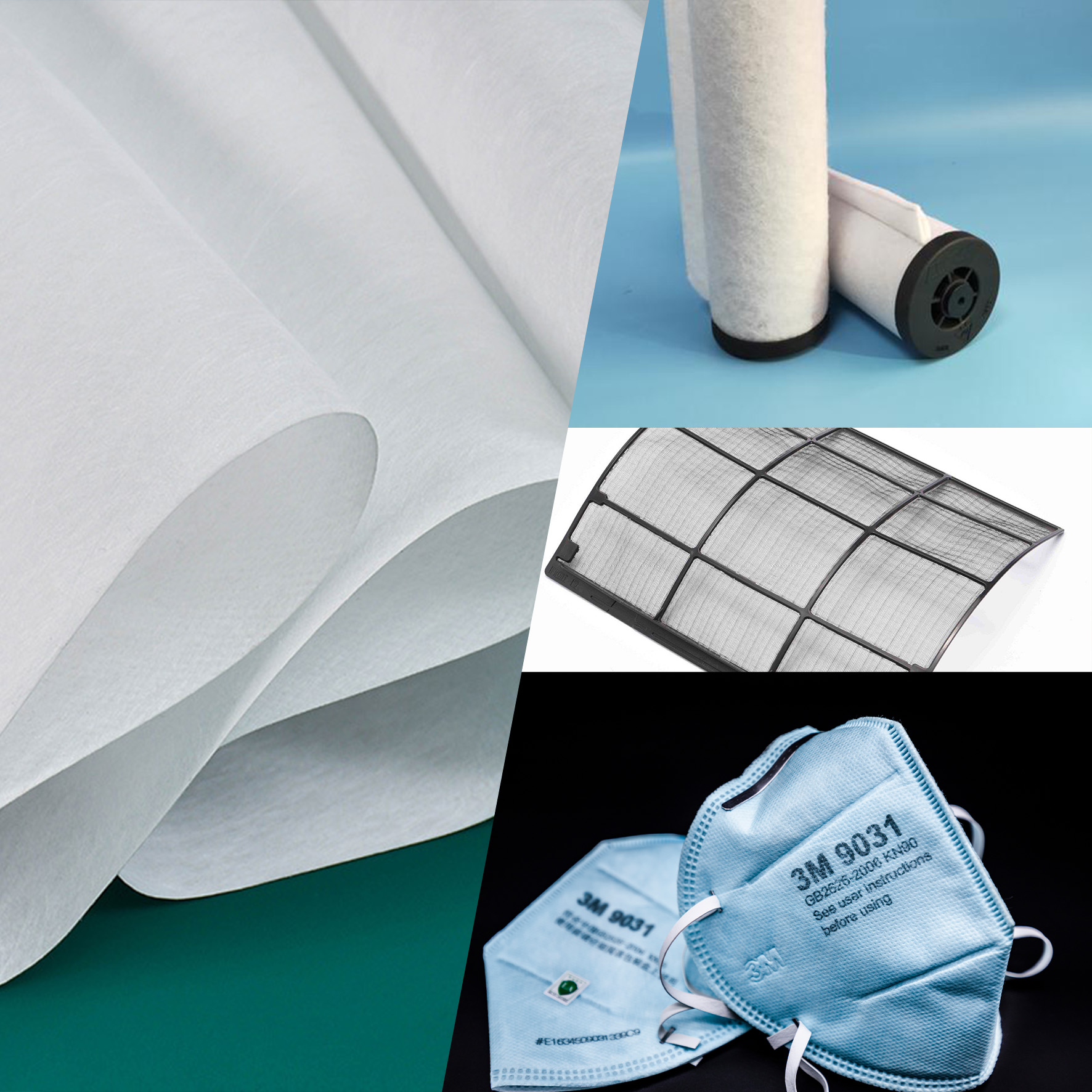

Meltblown nonwoven fabric became widely recognized during the global mask shortage, but its applications go far beyond medical use. This material has very fine fibers, excellent filtration properties, and a unique structure that sets it apart from other nonwovens. Whether you work in hygiene products, filtration, industrial wipes, or environmental protection, meltblown fabric plays a key role. In this article, I’ll walk you through its production process, types, features, and practical uses.
What Is Meltblown Nonwoven Fabric?
Meltblown nonwoven is a type of fabric made by extruding melted polymer—usually polypropylene—through extremely small nozzles. High-speed hot air stretches the fibers until they become ultra-fine, often just a few microns in diameter. These fibers fall randomly onto a conveyor belt and form a dense, web-like structure.
Because of these fine fibers, meltblown fabric has:
-
excellent filtration efficiency
-
high softness
-
strong absorption capability
-
very low linting
This makes it ideal for filters, masks, wipes, and oil-absorbent materials.
How Is Meltblown Fabric Manufactured?
1. Polymer Feeding and Melting
Most meltblown fabric uses polypropylene (PP). The polymer is melted and prepared for extrusion.
2. Fiber Formation
The molten polymer is pushed through a row of tiny nozzles. At the same time, hot air jets blow the fibers into ultra-thin strands.
3. Web Formation
The blown fibers land on a moving belt, creating a random, fluffy fiber web.
4. Bonding and Stabilizing
The web is lightly bonded using hot air or calendering to give the fabric its strength and uniformity.
5. Post-Treatment (Optional)
Depending on use, meltblown may undergo:
-
electrostatic charging (critical for mask filters)
-
hydrophobic or hydrophilic treatment
-
oil-absorbent finishing
Each treatment changes how the fabric performs in different industries.
What Makes Meltblown Fabric So Special?
Very Fine Fibers
Meltblown fibers are much thinner than spunbond fibers, which gives the material great filtering capability.
High Filtration Efficiency
Electrostatically charged meltblown fabric captures particles such as dust, bacteria, and aerosols without making breathing difficult. This is why it’s used in N95 and surgical mask filters.
Soft and Flexible
Despite its filtration strength, the fabric feels soft and lightweight.
Good Oil Absorption
The fine fiber structure allows meltblown to absorb many times its own weight in oil, making it useful for environmental cleanup.
Low Linting
It doesn’t easily shed fibers, which is important for medical and electronics applications.
What Types of Meltblown Fabric Are Common?
1. Standard Meltblown PP Fabric
Used for wipes, filtration layers, and absorbent materials.
2. Electrostatic Meltblown Fabric (ES/Meltblown)
Charged through corona or electret processes. Mainly used in mask filtration layers.
3. Water-Repellent Meltblown
Used in some hygiene or protective products where moisture control matters.
4. Oil-Absorbent Meltblown
Designed to quickly absorb oils—often used in industrial workshops or spill control products.
5. Composite Meltblown Structures
Sometimes combined with spunbond layers to form:
-
SMS
-
SMMS
-
SSMMS
These structures improve strength, filtration, and barrier performance.
What Are the Main Applications of Meltblown Nonwoven Fabric?
Face Masks and Respirators
Meltblown is the key filtration layer in:
-
N95
-
KN95
-
Surgical masks
-
Single-use medical masks
Without meltblown, these masks wouldn’t meet filtration standards.
Air and Liquid Filtration
The fine fibers help filter dust, bacteria, and even very small particles in:
-
air purifiers
-
HVAC systems
-
vacuum cleaner filters
-
industrial filtration systems
Absorbent Materials
Meltblown is widely used for:
-
oil cleanup pads
-
industrial absorbent rolls
-
marine spill control
Hygiene and Cleaning Products
Some wet wipes and household wipes include meltblown layers for improved absorbency or filtration.
Protective Apparel
Used in composite nonwoven structures for medical gowns and protective coveralls.
What Factors Affect Meltblown Fabric Quality?
Fiber Diameter
Finer fibers generally have better filtration performance.
Uniformity of the Web
A smooth, even surface indicates better processing quality.
Electrostatic Charge Stability
Especially important for filtration products—unstable charge reduces filtration efficiency over time.
Basis Weight (GSM)
Different GSM levels serve different purposes. Higher GSM typically offers better filtration or absorbency.
MFI (Melt Flow Index) of the PP
MFI affects how well the polymer forms fine fibers. High-MFI PP (1500+) is often used for meltblown.
How to Choose the Right Meltblown Fabric?
When selecting meltblown nonwoven fabric, consider:
-
final application (mask, filter, absorbent pad, wipe)
-
required filtration efficiency
-
whether electrostatic charge is needed
-
GSM requirement
-
oil absorption or hydrophobic property
-
compliance with local standards (ASTM, EN, GB)
A knowledgeable supplier should be able to match the correct specification to your product.
FAQ
Q1: Is meltblown fabric washable?
Generally no. Washing removes the electrostatic charge and damages the fiber structure, reducing filtration.
Q2: What GSM is used for mask filtration?
Commonly 20–30 GSM, depending on filtration requirements.
Q3: Is meltblown fabric environmentally friendly?
Standard PP meltblown is not biodegradable, but recycling options exist. Some newer bio-based versions are being developed.
Q4: What makes meltblown different from spunbond?
Spunbond fibers are thicker and stronger, while meltblown fibers are extremely fine and better for filtration.
Why Choose Shanghai Weboss New Material Technology Co.,Ltd.?
Shanghai Weboss New Material Technology Co.,Ltd. has years of experience supplying nonwoven fabrics—including meltblown, spunbond, SMS, and various composite materials—to customers worldwide. Our meltblown products are produced with stable MFI raw materials, strict quality control, and consistent filtration performance. Whether you need electrostatic meltblown for masks or absorbent-grade meltblown for industrial use, we provide reliable specifications, testing reports, and export-ready documentation.
We focus on stable supply, technical support, and long-term cooperation. If you’re looking for a dependable meltblown supplier, our team is ready to assist you.
continue reading
Related Posts
This article explains laminated nonwoven fabric, its structure, materials, functions, applications, and how to choose the right option for different uses.
Spunmelt nonwoven fabric is a multi-layered material combining spunbond and meltblown technologies to deliver strength, breathability, and barrier performance. Manufactured through polymer extrusion, web formation, bonding, and finishing, spunmelt fabrics can feature hydrophilic, anti-bacterial, anti-static, and “Three-Anti” treatments.
Spunlace nonwoven fabric is a mechanically bonded material produced by entangling fibers with high-pressure water jets rather than thermal or chemical bonding.






