What Should You Know About Spunmelt Nonwoven Fabric?
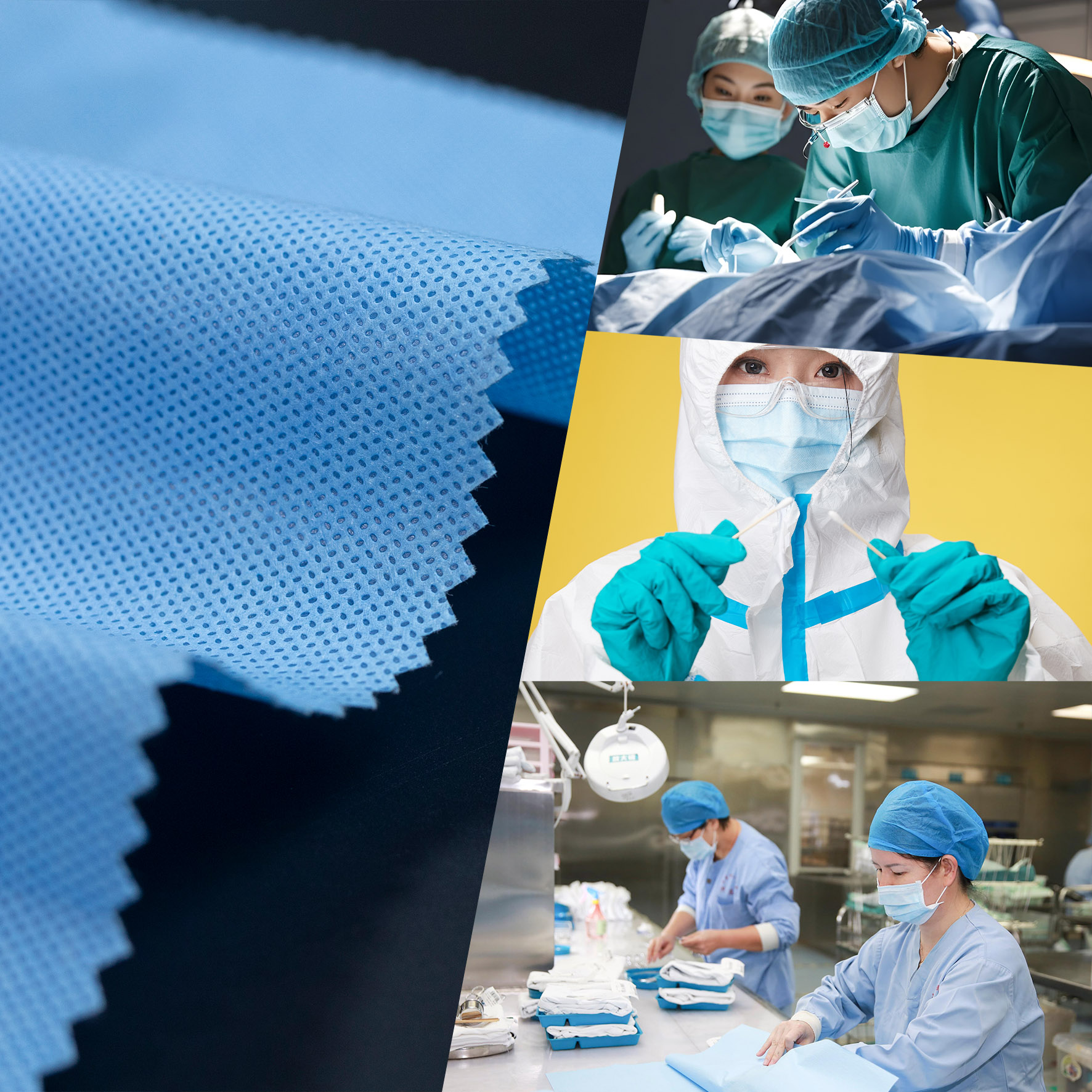
This article explains what spunmelt nonwoven fabric is, including its structures such as SMS, SMMS, SSMMS, and SMMMS, along with material properties, applications, and selection guidelines.
What Is Spunmelt Nonwoven Fabric?
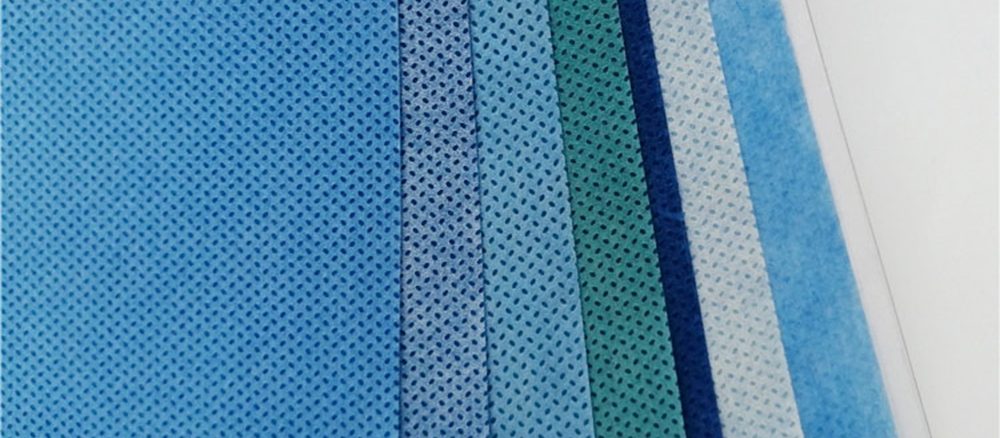
Spunmelt nonwoven fabric is a composite material made by combining spunbond (S) and meltblown (M) layers in various sequences such as SMS, SMMS, SSMMS, and SMMMS.
These fabrics integrate the strength of spunbond layers with the filtration and barrier properties of meltblown, making them ideal for medical, hygiene, industrial, and protective applications.
Spunmelt is widely recognized in high-performance nonwovens due to its balance of durability, filtration, softness, and breathability.
How Are Spunbond and Meltblown Layers Different?
Spunbond (S) Layer
-
Made from continuous filaments (usually PP)
-
Provides strength, durability, and structure
-
Good elongation and tensile performance
Meltblown (M) Layer
-
Made from microfibers
-
Provides filtration, barrier, and absorbency
-
Soft, fine, and ideal for blocking particles and droplets
Spunmelt fabrics are simply different combinations of these two technologies.
What Are the Main Types of Spunmelt Fabrics?
1. SMS (Spunbond–Meltblown–Spunbond)
-
Three layers
-
Strong + breathable + basic barrier
Used for: -
Medical gowns
-
Diaper backsheet
-
Basic protective apparel
2. SMMS (Spunbond–Meltblown–Meltblown–Spunbond)
-
Enhanced filtration due to double meltblown
Used for: -
Higher-level medical gowns
-
Surgical drapes
-
Hygiene core materials
3. SSMMS (Spunbond–Spunbond–Meltblown–Meltblown–Spunbond)
-
Extra spunbond layers for strength
-
Excellent uniformity and comfort
Used for: -
High-quality medical gowns
-
Premium hygiene materials
-
Industrial protective fabrics
4. SMMMS / SMMMMS (Multiple Meltblown Layers)
-
Very strong barrier performance
-
Soft, breathable, and strong
Used for: -
Level 3–4 medical PPE
-
High-level filtration and protection



What Materials Are Used for Spunmelt Nonwoven Fabric?
Spunmelt nonwoven fabric is mainly produced from thermoplastic polymers, with polypropylene (PP) being the dominant choice. Additional materials and additives can significantly enhance performance depending on final application requirements.
1. Primary Materials
-
PP (polypropylene) — the most widely used polymer for spunmelt fabrics
-
PE/PP blends — softer touch, often used in hygiene products
-
Medical-grade PP formulations — used for protective apparel and surgical materials
2. Functional Additives and Treatments
Depending on the application, spunmelt fabrics can undergo multiple finishing treatments:
For Hygiene & General Use
-
Hydrophilic Treatment — improves liquid absorption
-
Hydrophobic Treatment — enhances water repellency
-
Anti-Static Treatment — reduces static during processing
-
UV Resistant Additives — for agricultural and outdoor applications
-
Flame Retardant Additives — improves safety in industrial uses
For Medical & Protective Uses (Three-Resistance Finishing)
Medical-grade spunmelt can be engineered with Three-Resistance (3R) treatments, including:
-
Alcohol-Resistant — prevents penetration of alcohol-based liquids
-
Blood Plasma-Resistant — improves biological fluid protection
-
Oil / Body Fluid–Resistant — resists oils and body fluids
These treatments make spunmelt suitable for:
-
Surgical gowns
-
Isolation gowns
-
Protective coveralls
-
Medical drapes
They also help fabrics meet standards such as AAMI PB70, EN 13795, and other global medical safety regulations.
What Are the Key Properties of Spunmelt Fabrics?
-
High tensile strength (from spunbond layers)
-
Excellent filtration & barrier (from meltblown layers)
-
Soft and skin-friendly
-
Breathable yet protective
-
Highly uniform web structure
-
Customizable absorbency and repellency
-
Stable performance in lamination and printing
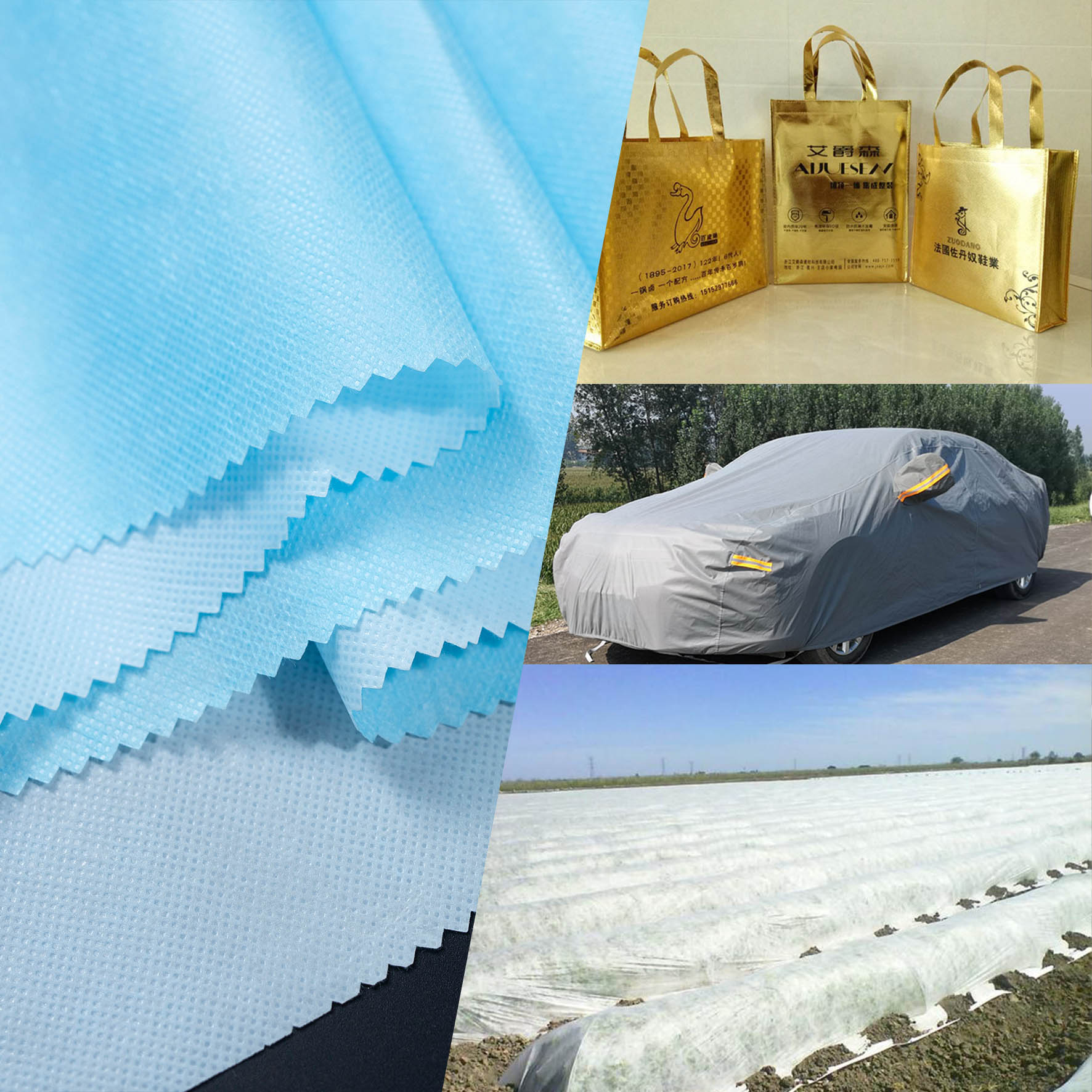
Where Are Spunmelt Nonwovens Used?
1. Medical & Healthcare
-
Surgical gowns
-
Isolation gowns
-
Medical masks (inner/outer layers)
-
Drapes and wraps
2. Hygiene Products
-
Baby diapers
-
Adult incontinence products
-
Sanitary napkins
-
Hygiene cores & backsheets
3. Industrial Protection
-
Coveralls
-
Chemical-resistant apparel
-
Workwear interlining
4. Filtration
-
Air filtration
-
Dust collection
-
Liquid filtration
5. Agriculture
-
Crop covers
-
Greenhouse shading materials
How to Choose the Right Spunmelt Structure?
| Structure | Key Strength | Application Level |
|---|---|---|
| SMS | Basic barrier | Standard hygiene & basic medical |
| SMMS | Higher filtration | Surgical drapes, improved diapers |
| SSMMS | Strength + softness | High-level medical gowns |
| SMMMS | Maximum protection | Medical PPE & industrial suits |
Selection Tips
-
Define required barrier level.
-
Choose softness for skin-contact applications.
-
Select appropriate GSM (15–100 gsm).
-
Request sample testing for bonding performance.
-
Confirm finishing treatments, especially for medical fabrics.
FAQ
Q1: Is spunmelt nonwoven waterproof?
A: It is water-repellent but not fully waterproof unless laminated.
Q2: Which structure is best for medical gowns?
A: SMMS and SSMMS are preferred for higher barrier and softness.
Q3: Can spunmelt be used for masks?
A: Yes, but mainly as structural layers; filtration requires specialized meltblown.
Q4: Is spunmelt breathable?
A: Yes, it provides airflow while maintaining protective performance.
Q5: Can spunmelt fabrics be customized?
A: Yes—GSM, softness, hydrophilicity, and 3R medical treatments can all be customized.
Why Choose Shanghai Weboss New Material Technology Co.,Ltd. for Spunmelt Nonwoven Fabric?
-
Full Range of SMS/SMMS/SSMMS Fabrics: Customized to meet different performance levels.
-
Medical & Hygiene Expertise: Three-resistance (alcohol, blood, oil) finishing available.
-
Stable Quality: Uniform web structure and consistent GSM control.
-
Professional Treatments: Hydrophilic, hydrophobic, antistatic, UV-resistant, and flame retardant.
-
Global Supply Capacity: Reliable delivery to Europe, America, and South America.
Shanghai Weboss New Material Technology Co.,Ltd. provides stable performance, competitive pricing, and long-term support for your spunmelt nonwoven fabric needs.
continue reading
Related Posts
This article explains laminated nonwoven fabric, its structure, materials, functions, applications, and how to choose the right option for different uses.
Spunmelt nonwoven fabric is a multi-layered material combining spunbond and meltblown technologies to deliver strength, breathability, and barrier performance. Manufactured through polymer extrusion, web formation, bonding, and finishing, spunmelt fabrics can feature hydrophilic, anti-bacterial, anti-static, and “Three-Anti” treatments.
Spunlace nonwoven fabric is a mechanically bonded material produced by entangling fibers with high-pressure water jets rather than thermal or chemical bonding.





